The banking sector has undergone a massive digital transformation over the last two decades. From mobile banking apps to AI-powered fraud detection, technology has redefined how banks operate and engage with customers. But there’s one innovation quietly reshaping the financial landscape faster than most people realize; Robotic Process Automation in Banking.
Robotic automation in banking is not about physical robots with metallic arms counting cash in vaults. Instead, it’s about software robots or “bots”, that can replicate human tasks in banking operations. These bots can log into systems, enter and extract data, process transactions, generate reports, and even communicate with customers. The result? Faster, error-free, and more cost-effective banking processes.
Recent reports suggest that banks using RPA automation in banking can reduce operational costs by up to 25–50%, with ROI often achieved within the first year of implementation. A Gartner study projects that by 2026, over 90% of global banks will have adopted some form of RPA in the banking industry to streamline processes and enhance customer service.
From automating compliance reporting to speeding up loan approvals, robotic process automation use cases in banking are becoming a game-changer. Not just for large banks but also for mid-sized and regional institutions aiming to stay competitive. In a world where customers expect instant services and regulators demand meticulous accuracy, RPA provides a bridge between efficiency and compliance.
In this article, we’ll explore what is robotic process automation in banking, how it differs from traditional automation, examples of RPA in banking, benefits, challenges, and where it’s headed in the future.
What is Robotic Process Automation in Banking?
At its core, Robotic process automation in banking refers to the use of software bots to perform repetitive, rule-based banking tasks without human intervention. These tasks might involve data entry, account verification, transaction processing, or regulatory reporting, essentially anything that can be defined by a set of clear, repeatable rules.
Unlike traditional automation, which often requires complex coding and rigid system integration, RPA automation in banking uses a “non-invasive” approach. Bots interact with applications just like a human would, clicking, typing, copying, and pasting, but at a much faster pace and without fatigue. This means RPA can work with legacy banking systems without requiring costly overhauls.
Key difference between traditional automation vs. RPA in banking:
| Feature | Traditional Automation | Robotic Process Automation |
| Implementation | Requires coding & deep integration | Low-code or no-code setup |
| Flexibility | Limited; works for specific processes | Highly adaptable to different workflows |
| Interaction | Works within back-end systems | Works through the user interface like a human |
| Scalability | Often slow to scale | Easily scalable with additional bots |
For example, a traditional automated system might be hardwired to pull customer data from a database, while an RPA in banking industry bot can log into multiple applications, extract data, cross-check it, and upload it to another platform, all without any changes to the core systems.
Banks prefer RPA because it reduces the reliance on expensive IT overhauls and enables quick wins with minimal disruption. In essence, it’s like hiring a digital employee that works 24/7, never makes a typo, and can be duplicated instantly when needed.
Role of RPA in Banking Industry
In the fast-paced banking industry, delays and errors can cost millions, not just in money, but in customer trust and regulatory penalties. The role of RPA in banking is to act as a force multiplier for efficiency, accuracy, and compliance.
- Streamlining Operations & Compliance: Robotic automation in banking helps handle high-volume tasks such as Know Your Customer (KYC) verification, anti-money laundering (AML) checks, and compliance reporting. These are mandatory processes with strict deadlines. Bots, often deployed via managed automation services, ensure that every report is accurate, complete, and delivered on time; reducing the risk of costly compliance failures.
- Reducing Manual Errors: Manual data entry and cross-verification can lead to human errors. Even a single misplaced decimal in a financial statement can have serious consequences. RPA bots eliminate such mistakes, ensuring consistent, high-quality output every time.
- Increasing Efficiency: Imagine processing thousands of loan applications or payment requests in minutes instead of days. With RPA automation in banking, this is possible. Bots don’t take coffee breaks, don’t get tired, and can work on multiple tasks simultaneously; drastically increasing operational throughput.
RPA’s role is not to replace bankers entirely but to augment human capabilities. Employees can then focus on high-value tasks like customer relationship management, financial planning, and strategic decision-making while bots handle the repetitive, rule-based processes.
Top Applications & Use Cases of RPA in Banking Industry
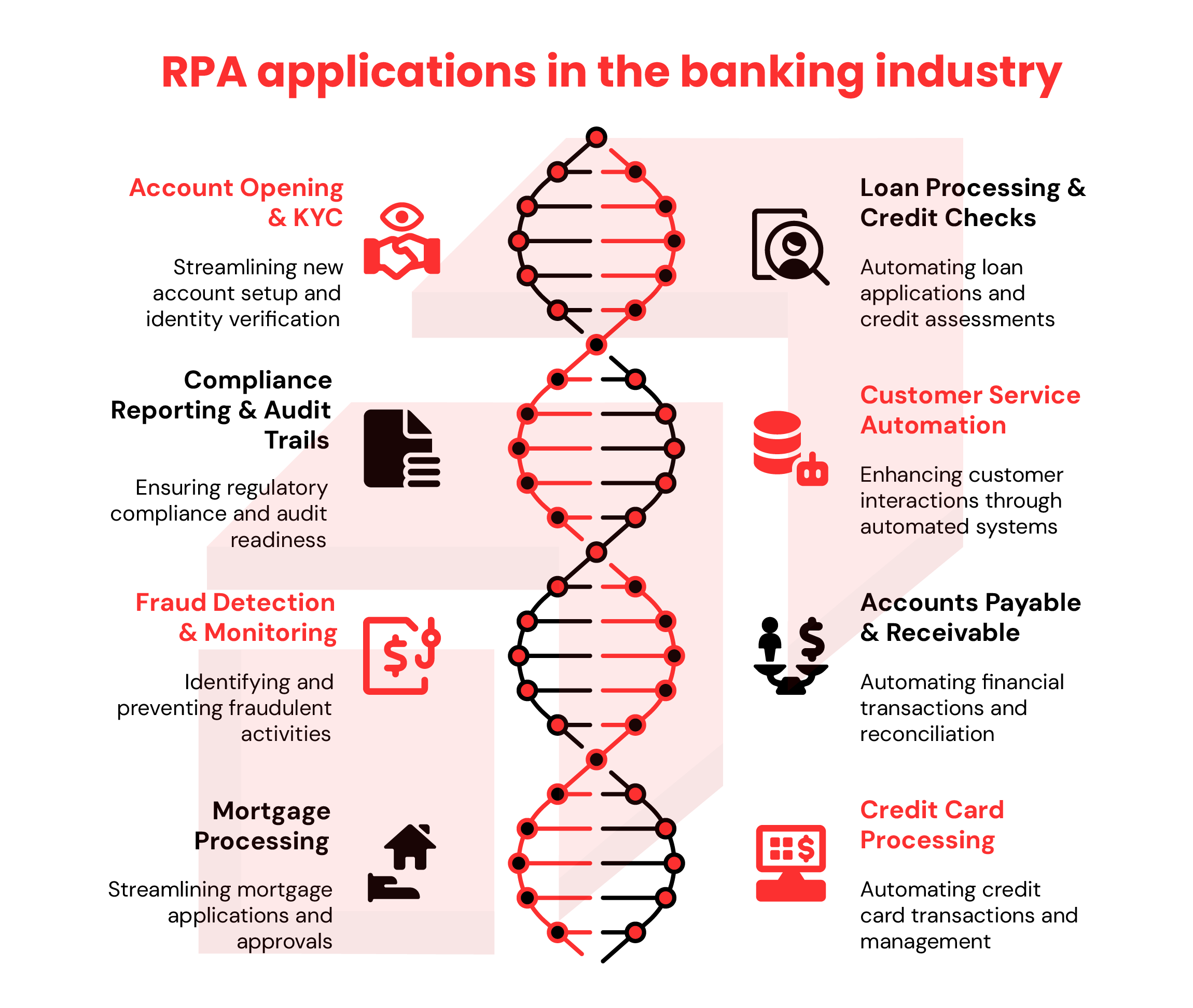
The rpa applications in banking industry are vast, but here are some of the most impactful robotic process automation use cases in banking:
Account Opening & KYC Verification
Bots can instantly verify customer details, validate documents, and update records; cutting onboarding times from days to minutes.
Loan Processing & Credit Checks
RPA automation in banking can pull data from credit bureaus, verify income details, and process approvals without manual intervention.
Compliance Reporting & Audit Trails
Bots ensure every transaction and report is logged, timestamped, and compliant with regulations.
Customer Service Automation
Integrated with chatbots, RPA can resolve common customer queries instantly; from account balance requests to transaction history lookups.
Fraud Detection & Monitoring
Bots can flag unusual transactions in real time, helping fraud teams act before damage is done.
Accounts Payable & Receivable Automation
Robotic automation in banking can match invoices with purchase orders, process vendor payments, and reconcile accounts automatically.
Mortgage Processing
Document-heavy mortgage approvals can be streamlined, reducing turnaround times by weeks.
Credit Card Processing
From application verification to activation, bots can handle the full credit card lifecycle.
These RPA in banking use cases illustrate why the technology is becoming an indispensable tool; speeding up processes, ensuring accuracy, and freeing human staff for more complex tasks.
Examples of RPA in Banking
Real-world adoption of RPA in banking industry shows just how powerful the technology can be: Below are the few robotic process automation examples in banking sector
- JPMorgan Chase uses robotic automation in banking for legal document reviews, reducing 360,000 hours of manual work annually.
- ICICI Bank in India deployed over 750 bots for processes like account closure, compliance, and customer onboarding; cutting turnaround times drastically.
- Deutsche Bank integrates RPA in trade settlement processes, ensuring faster execution with fewer errors.
- ANZ Bank uses bots for mortgage processing, slashing approval times and improving customer satisfaction.
In each case, the results are lower operational costs, higher accuracy, and faster service delivery; proving that RPA automation in banking isn’t just a tech trend but a critical driver of competitive advantage.
Benefits of RPA in Banking
The benefits of Robotic Process Automation in Banking extend far beyond cost savings, they shape efficiency, compliance, and customer engagement in profound ways.
Automates Repetitive, Time-Consuming Tasks
From monthly statement generation to RPA automation in banking for KYC checks, bots’ complete tasks in minutes that would take humans hours. This frees up staff to focus on high-value, customer-facing work.
Reduces Operational Costs
By replacing manual workflows with robotic automation in banking, operational costs can drop by 25–50%. Savings can then be reinvested in innovation or competitive pricing.
Eliminates Human Errors
RPA in banking industry ensures every process, from data entry to reconciliation, is executed with perfect accuracy, reducing costly compliance issues.
Enhances Customer Experience
Faster loan approvals, instant account activation, and quicker query resolution keep customers satisfied.
Speeds Up Critical Processes
KYC verification, fraud detection, and credit approvals happen in real time.
Ensures Regulatory Compliance
Every transaction managed by bots is logged, creating a reliable audit trail.
Seamless Legacy Integration
Robotic process automation in banking industry works with existing systems without costly overhauls.
Scalability During Peak Periods
Add more bots during high-demand seasons, like tax time, without extra hiring.
Boosts Employee Productivity
By automating mundane tasks, banks unlock staff potential for strategic projects.
Supports Business Continuity
Even during crises, bots maintain uninterrupted services.
Quick ROI
Many banks see returns on RPA automation in banking within 6–12 months.
Competitive Edge
Fast, error-free services help banks stand out in saturated markets.
Challenges & Limitations
Even with the strong appeal of RPA in banking industry, challenges remain.
- Unstructured Data Limitations: Bots struggle with unformatted or handwritten inputs unless paired with AI.
- Integration Issues: Legacy systems can make robotic automation in banking rollouts complex.
- High Initial Setup: Mapping processes and training bots takes time.
- Workflow Sensitivity: System changes can cause RPA automation in banking bots to fail without updates.
- Scalability Without AI: Rules-based bots can’t make human-like decisions.
- Ongoing Maintenance: Bots require constant monitoring to keep up with regulation shifts.
- Decision-Making Limitations: Some tasks still need human judgment.
- Security Concerns: Improper bot permissions could open security gaps.
- Compliance Risks: Misconfigured bots can create incorrect regulatory outputs.
- Skills Gap: Not all banking teams have trained RPA specialists. \
- Cultural Resistance: Staff may fear RPA automation in banking will replace jobs.
- Overdependence Risks: Sole reliance on bots can be dangerous if systems fail.
- Executive Hesitation: Some leaders delay scaling beyond initial projects.
The Future of RPA in Banking Sector
The future isn’t just robotic process automation in banking; it’s hyper-automation. A place where AI, machine learning, and NLP combine with RPA for smarter workflows.
AI + RPA Synergy: Enhanced decision-making and exception handling.
Chatbot & NLP Integration: Seamless conversational banking powered by robotic automation in banking.
Predictive Automation: Anticipating compliance and service needs before they arise.
Tier-Based Adoption
- Tier 1 banks: AI + RPA for large-scale transformation.
- Tier 2 banks: Expanding RPA automation in banking to remain competitive.
- Tier 3 banks: Cloud-based RPA for affordable digital growth.
Regulation-First Automation: Bots ensuring continuous compliance.
BaaS Enablement: Robotic process automation use cases in banking enabling faster, modular product launches.
How to Implement RPA in Your Banking Workflow
To integrate RPA automation in banking effectively:
- Assess: Identify repetitive, high-volume processes.
- Tool Selection: Choose a platform compatible with RPA in banking industry and existing systems.
- Pilot Project: Start with a focused process like onboarding or compliance.
- Process Mapping: Document every step for accurate bot training.
- Development & Testing: Run bots in test environments before going live.
- Deployment: Launch bots alongside staff to ensure smooth transitions.
- Monitoring & Optimization: Review regularly to improve efficiency.
- Scaling: Expand to other processes across the robotic process automation in banking industry for maximum impact.
Conclusion
Robotic process automation in banking has evolved from an emerging technology into a strategic necessity. By automating high-volume, rule-based processes, banks are achieving faster turnaround times, reduced errors, improved compliance, and significant cost savings.
It’s important to note that RPA in banking industry is not just about efficiency, it’s also about regulatory accuracy and customer satisfaction. Bots can maintain continuous operations, process thousands of transactions flawlessly, and create detailed audit trails for compliance.
However, to fully unlock its potential, banks must approach RPA automation in banking strategically. This means integrating it with AI, machine learning, and NLP to move toward hyper-automation; where both routine and complex workflows are automated intelligently.
Looking ahead, robotic automation in banking will be essential for every tier of financial institutions. Tier 1 banks will lead with AI-powered RPA, Tier 2 will expand adoption for competitive advantage, and Tier 3 will leverage cloud-based RPA for affordability.
The future of finance will be faster, smarter, and more customer-centric, and robotic process automation in banking industry will be the cornerstone of that transformation.
Related Posts
Questions to Ask Before Adopting Cloud for FinTech | Challenges Faced by Fintech Companies | Cloud Technology and Banking | Cloud Technology in Insurance Industry | Top 5 Mistakes Neo-banking Should Avoid | How Cloud Technology Is Transforming Fintech | Cloud Computing For Banking Industry







