In an era when business agility and digital transformation are more critical than ever, the choice between a public and private cloud environment is a strategic decision. As you plan for 2026 and beyond, understanding how each model aligns with your goals is essential. Whether you’re weighing public cloud vs private cloud or exploring private cloud versus public cloud, this guide will help illustrate which environment may best serve your evolving enterprise needs.
The Cloud Landscape
The cloud computing landscape continues to evolve rapidly. At its core, cloud computing allows organisations to access compute, storage, networking and advanced services over the internet rather than relying solely on on-premises infrastructure.
Within this realm, the two primary deployment models are the public cloud and the private cloud. The public cloud delivers resources via a service provider to multiple tenants, offering high scalability and agility.
The private cloud offers a dedicated environment for a single organisation, delivering greater control, customisation and often enhanced security. Understanding how these models differ, and how they will evolve into 2026; is vital for shaping your cloud strategy.
What is Public Cloud and Private Cloud?
Public cloud gives organisations on-demand access to shared infrastructure managed by a cloud provider, ideal for rapid scaling and cost-efficient innovation. Whereas a Private cloud delivers a secure, dedicated environment tailored to one organisation, offering greater control, compliance readiness and custom architecture.
Key Differences Between Public and Private Cloud
At a high level, the difference between public vs private cloud lies in ownership, tenancy, control, cost model and operational model. The public cloud offers multi-tenant shared infrastructure, pay-as-you-go pricing and rapid provisioning. The private cloud offers a single‐tenant dedicated infrastructure, greater customisation and often greater up‐front investment.
As we approach 2026, shifts in regulation (data sovereignty), workload types (AI, edge) and cost transparency are intensifying these differences.
A Direct Comparison of Public Cloud vs Private Cloud
| Feature | Public Cloud | Private Cloud |
| Cost Model and Investment | Features pay-as-you-go, minimal upfront capital investment, strong for unpredictable workloads. In 2026 the public cloud market is forecast to continue growing significantly (market value near ~$947 billion) | Requires higher upfront investment or dedicated infrastructure, but grants cost predictability, fixed overhead and suited for stable workloads. |
| Scalability and Elasticity | Excellent elasticity, resources can scale up/down rapidly, ideal for bursty workloads, seasonal demand and innovation projects.
With trends like AI and edge pushing demands, public cloud shines. |
Scalability is possible, but often slower due to physical infrastructure or dedicated capacity. |
| Security and Control | Shared infrastructure implies less direct control over underlying hardware; security depends on provider controls and shared responsibility. | Greater control and visibility into infrastructure, custom security policies, data residency, and isolation. Particularly important for regulated industries or those needing high assurance. |
| Performance and Reliability | Providers operate large-scale networks and data centres offering high availability, global reach and rapid innovation. Public cloud offers fast time-to-market. | Because infrastructure is dedicated, performance can be more consistent, and reliability may be more predictable. |
| Management and Maintenance | Much of the infrastructure management is handled by the cloud provider, reduces internal overhead for IT teams. | The organisation has to manage or oversee the dedicated infrastructure. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Public cloud providers are rapidly building compliance frameworks and certifications. | Offers more straightforward alignment with strict regulatory, data-residency, sovereign-cloud or compliance regimes. |
When to Choose Public Cloud
Ideal for:
- Rapid innovation, test-and-learn projects or startups that require fast market entry.
- Highly variable workloads needing elastic capacity.
- Organisations seeking to minimise capital expenditure and outsource infrastructure management.
- Global geographic expansion, edge applications, or dynamic scaling across regions.
Advantages:
- Lower barrier to entry and faster deployment.
- Massive service ecosystem enabling rapid application modernisation.
- Pay-as-you-go cost model that aligns spend with usage.
- Ideal for workloads where agility, scale and innovation are core business differentiators.
When to Choose Private Cloud
Ideal for:
- Organisations in highly regulated industries with strict control.
- Workloads that require predictable performance, high latency sensitivity.
- Applications that have stable demand and where cost of change is high.
- Enterprises with existing strong IT infrastructure and intent to customise.
Advantages:
- Greater control over hardware, architecture, security posture and compliance.
- Predictable performance and cost for steady-state workloads.
- Better suited to sovereignty, data-residency or internal governance mandates.
The Rise of Hybrid & Multi-Cloud Strategies
As we approach 2026, it’s no longer a simple “public vs private cloud” decision. Many organisations choose a hybrid or multi-cloud model that combines the best of both.
Hybrid cloud models blend public cloud for innovation and elastically scaling parts of the business, with private cloud for control, sensitive workloads and legacy systems. Multi-cloud introduces the flexibility of multiple public or private cloud providers to avoid vendor lock-in and optimise workload placement. In fact, industry research suggests that hybrid and multi-cloud adoption will be widespread by 2026. For modern enterprise architectures, adopting a “right-cloud” or “fit-for-purpose” mindset, placing each workload in the best model; is becoming best practice.
Learn more – Exploring Different Cloud Computing Models: Public, Private, and Hybrid
How to Choose the Right Cloud Model
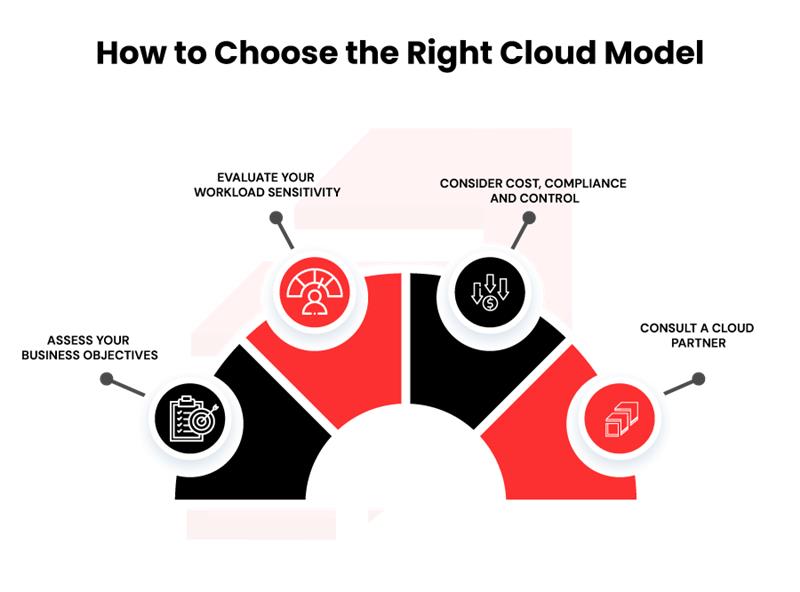
- Assess Your Business Objectives
Begin by clarifying your strategic goals: innovation speed, global reach, cost efficiency, regulatory compliance, or digital transformation. Understanding the drivers helps shape which cloud model aligns. - Evaluate Your Workload Sensitivity
Classify workloads by criticality, latency requirements, data sensitivity, compliance/regulation exposure, and expected growth. For example, highly sensitive corporate data or regulated workloads might favour private cloud, while public-facing apps may excel in public cloud. - Consider Cost, Compliance and Control
Analyse not just upfront cost, but ongoing operational cost, scaling behaviour, governance overhead, compliance burden and vendor lock-in risk. Public cloud may offer agility but less direct control; private cloud offers control but may require higher internal operations investment. - Consult a Cloud Partner
Partnering with a cloud consulting or managed-services provider can help you navigate complexity, build the right architecture, and align cloud adoption with business goals. Especially as cloud-native, edge and hybrid strategies become more complex, expert guidance adds value.
Rapyder’s Recommendation
At Rapyder, we recommend a pragmatic “workload-first” approach to cloud adoption in 2026. Rather than defaulting to one model, we evaluate each application’s needs; cost behaviour, security posture, scalability demands and compliance footprint, and recommend the optimal placement: public, private or hybrid.
We also emphasise the importance of FinOps, data sovereignty and sustainability as strategic levers. By partnering with Rapyder, organisations can build a future-proof cloud roadmap that positions you for 2026 and beyond.
Conclusion
As you plan for 2026, look beyond base features and ask: which model best aligns with workload profile, regulatory demands, scalability needs, and cost behaviour?
Public cloud offers scale, speed and innovation. Private cloud offers control, customisation and compliance assurance. Many organisations will find the answer in a hybrid or multi-cloud strategy that combines both. Ultimately, aligning your cloud choice with business strategy will ensure you’re powering your business for the future.
Looking to Find the Right Cloud Strategy for Your Business?
If you’re ready to navigate the complex world of cloud infrastructure and ensure your business is positioned for success in 2026, Rapyder is here to help.
We specialise in guiding organisations through the choice of public, private and hybrid cloud, crafting customised roadmaps that align with your business objectives, workloads and compliance needs. Connect with us today to build a cloud strategy that powers your growth and digital transformation.







