Think of AWS RDS and Amazon Aurora as two heavyweight fighters in the ring of relational databases, each with its own fighting style.
AWS RDS is the dependable veteran: battle-tested, flexible, and well-known. Aurora, on the other hand, is the sleek, high-octane sprinter built for the cloud: fast, scalable, and ruthless when it comes to performance.
As you plan your data-layer strategy for 2026 and beyond, choosing between AWS RDS vs Aurora isn’t just about capacity; it’s about speed, resilience, and cost efficiency that match your business’s growth trajectory.
In this blog, you will understand the difference between Aurora and RDS & how to choose the best option for Your Business
Understand the Difference between AWS RDS and Aurora
Before we dive in, let’s clarify what each service actually is.
What is AWS RDS?
Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service) is AWS’s managed relational database service. It supports a variety of database engines, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, Oracle, and MariaDB, giving you flexibility. With RDS, AWS handles administrative tasks like backups, patching, and monitoring, so you can concentrate on your application, not database mai
ntenance.
What is Amazon Aurora?
Amazon Aurora is a cloud-native relational database designed to be compatible with MySQL and PostgreSQL. But unlike a traditional RDS engine, Aurora uses a distributed, highly available storage layer that decouples compute and storage. This architecture delivers high throughput, better fault-tolerance, and seamless scaling.
Key Difference Between Aurora and RDS
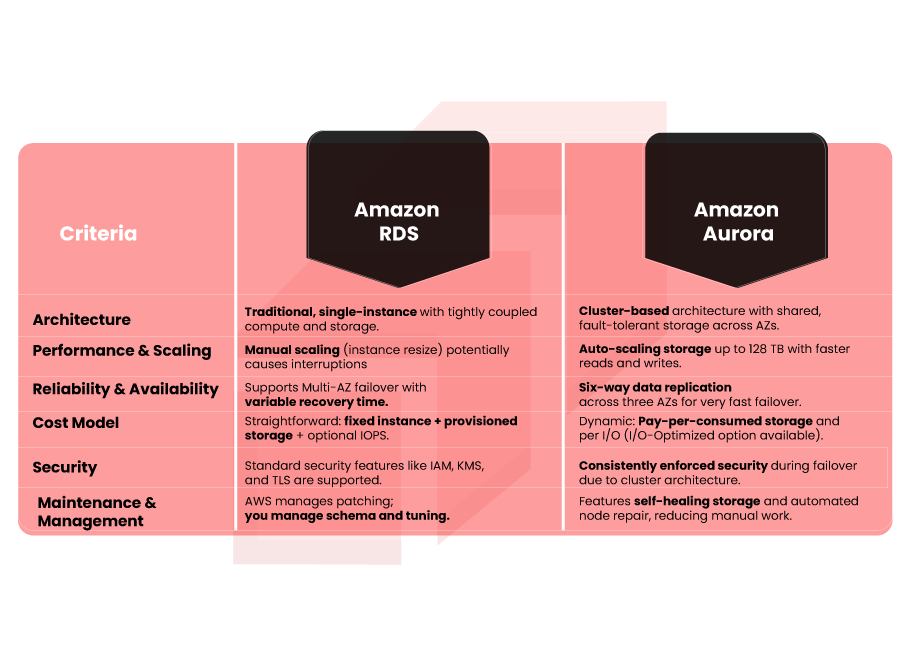 When comparing Amazon Aurora vs RDS, the differences run deep; not just in pricing, but in architecture, performance, availability, and more.
When comparing Amazon Aurora vs RDS, the differences run deep; not just in pricing, but in architecture, performance, availability, and more.
Architecture
- RDS: Uses a more traditional, single-instance architecture where compute (DB instance) and storage are tightly coupled. You can use read replicas for scaling reads, but each replica maintains its own copy of data.
- Aurora: Employs a cluster-based architecture: multiple compute instances (writers and readers) attach to a shared storage layer that spans Availability Zones. This distributed storage is fault-tolerant and abstracts away complexity.
Performance & Scaling (Aurora vs Rds Performance)
- RDS: Scaling up involves resizing the instance type or adding read replicas, but storage scaling is more manual. This may lead to interruptions or performance trade-offs.
- Aurora: Thanks to its decoupled architecture, Aurora offers faster reads and writes. One of the most powerful features is its auto-scaling storage, which can grow from as little as 10 GB to up to 128 TB, all without downtime.
Reliability & Availability
- RDS: Supports Multi-AZ deployments for high availability. In case of failure, AWS automatically fails over to a standby instance, but failover may take some time depending on the engine and workload.
- Aurora: Replicates data six times across three AZs, which makes it highly resilient. Failovers are typically fast, and thanks to its cluster architecture, Aurora recovers quickly.
Aurora also supports Global Databases, enabling low-latency reads from other AWS Regions, great for disaster recovery and geo-distributed applications.
Cost Model (Aurora vs RDS pricing)
- RDS: Pricing is straightforward: you pay for the DB instance + provisioned storage + IOPS (if you choose provisioned IOPS). Reserved instances can lower costs for steady workloads.
- Aurora: Uses a more dynamic cost model:
– Instance cost: Hourly charge based on instance type.
– Storage cost: You pay only for the storage you consume.
-I/O Requests: Depends on the configuration:
-Aurora Standard: Pay-per-I/O operations (reads and writes).
– Aurora I/O-Optimized: No separate I/O billing. I/Os are bundled into the storage cost, giving more predictable pricing.
– Serverless Option: Aurora Serverless v2 lets you pay per Aurora Capacity Unit.
-Cost Efficiency: For I/O-intensive workloads, Aurora can be highly cost-efficient, especially with the I/O-Optimized option, which reduces unpredic I/O billing.
Security
- Both RDS and Aurora support AWS IAM for access control, KMS encryption, and TLS for data-in-transit.
- Aurora benefits from its cluster architecture for rapid failover, meaning security controls remain consistently enforced even during high-availability events.
Maintenance & Management
- RDS: AWS handles administrative tasks like backups, patching, and monitoring. You still manage schema, queries, and database-level tuning.
- Aurora: Because of its cloud-native architecture, Aurora offers self-healing storage, continuous backups, and even automated repair of storage nodes; reducing manual intervention and enhancing reliability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business
Deciding between Aurora vs RDS isn’t just a technical choice, it’s a business decision. Here’s how to pick based on your needs:
Choose RDS if:
- You run predictable workloads with moderate performance needs and don’t need massive scale.
- You require multiple database engines (Oracle, SQL Server, MariaDB) that Aurora doesn’t support.
- Cost control is a priority, RDS’s instance + storage billing is simpler and often lower for smaller workloads or development environments.
- You don’t need ultra-fast failover or global scaling, traditional Multi-AZ RDS is often sufficient for many business apps.
Choose Aurora if:
- You are building high-throughput, mission-critical applications, such as SaaS platforms, e-commerce back ends, or real-time analytics, where performance matters.
- You expect massive growth in storage or unpredictable spikes in database size: Aurora’s storage auto-scaling removes provisioning risk.
- High availability is non-negotiable: Aurora replicates across AZs and provides very fast failover.
- You want predictable I/O costs: Aurora’s I/O-Optimized configuration is built for workloads with high I/O demands and provides cost stability.
- You want to leverage Serverless Aurora: for workloads that are bursty or variable, paying by ACU (capacity unit) offers flexibility and potential savings.
Rapyder’s Expertise in AWS Database Consulting
At Rapyder, we’re more than just cloud experts, we’re your strategic partner for database innovation. When you face the difference between AWS RDS and Aurora, we don’t just recommend; we architect. Our team helps you:
- Assess workload patterns to decide whether RDS, Aurora or a hybrid is the best fit.
- Plan migration paths, whether lifting and shifting from RDS to Aurora or building fresh clusters.
- Optimize cost using Aurora’s I/O-Optimized configurations or reserved pricing, aligning with your traffic and query patterns.
- Tune for performance and availability, leveraging Aurora’s replicas, clustering, or serverless modes.
- Manage ongoing operations, with automated backup strategies, performance insights, and self-healing storage to reduce manual toil.
Let Rapyder guide your database journey so that you get maximum performance, resilience, and efficiency, all powered by either Amazon Aurora or RDS, whichever aligns best with your 2026 business goals.
Final Thoughts
In the Aurora vs RDS debate, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer. RDS remains a stalwart choice for predictable, stable workloads with fewer frills. But if you’re building for scale, performance, and automatic resilience, Amazon Aurora delivers superior throughput, storage flexibility, and high availability with a compelling cost model for demanding applications. Backed by Rapyder’s AWS consulting expertise, you can choose the right engine and set your data architecture up for sustained growth.







