AWS offers multiple powerful database services, and choosing the right one can significantly influence your application’s performance and scalability. Among the most compared options is Amazon Aurora vs DynamoDB, a comparison many teams explore when deciding how to structure their data layer.
This blog breaks down the essentials of amazon aurora vs dynamodb, clarifies their architectural differences, and helps you choose the right AWS database for your use case.
What is Amazon Aurora?
Amazon Aurora is AWS’s fully managed, high-performance relational database engine designed to deliver the speed and reliability of traditional commercial databases – minus the heavy licensing fees. When comparing AWS Aurora vs DynamoDB, Aurora often shines for workloads that need strong relational capabilities, full SQL support, and compatibility with MySQL or PostgreSQL, all while offering up to five times the throughput of standard MySQL.
Aurora’s real strength lies in its balance of performance, availability, and ease of use. It automatically stores six copies of your data across three Availability Zones, giving you built-in durability without extra operational overhead. With features like Aurora Serverless, capacity scales up or down based on real-time traffic, making it perfect for variable or unpredictable workloads. For teams looking for enterprise-grade performance with true cloud-native flexibility, Aurora remains one of the most compelling database choices on AWS.
What is Amazon DynamoDB?
Amazon DynamoDB is a fully managed NoSQL database service designed for massive scale, high availability, and single-digit millisecond performance. Unlike relational databases, DynamoDB uses a key-value and document data model, making it ideal for applications requiring flexible schemas or handling enormous volumes of read/write operations.
DynamoDB automatically manages throughput, partitions, replication, and scaling with zero operational overhead. With features like DynamoDB Streams, Global Tables, on-demand capacity, and DAX caching, it powers applications requiring ultra-fast, predictable performance across regions. It’s a favorite among modern, serverless, event-driven, and real-time systems where low latency at scale is crucial.
Difference Between Aurora vs DynamoDB
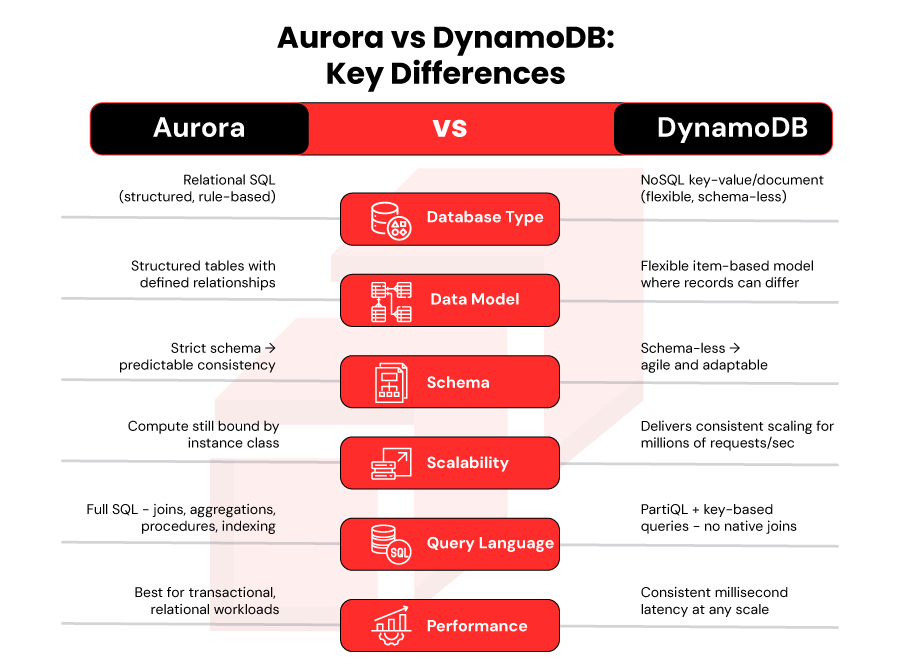
To truly understand aws aurora vs dynamodb, it’s essential to look at how both services differ across architecture, data models, performance profiles, and scaling behavior. Below is a clear comparison to help you evaluate which database aligns best with your application’s requirements.
Key Differences Explained
Database Type
Aurora is a relational SQL database, while DynamoDB is a NoSQL key-value/document store. This is the biggest differentiator: Aurora enforces relationships; DynamoDB embraces flexibility.
Data Model
Aurora stores data in structured tables with defined relationships using primary and foreign keys. DynamoDB stores items with flexible attributes, each record can look different, ideal for evolving data structures.
Schema
Aurora requires a strict schema, making it perfect for applications needing data consistency. DynamoDB’s schema-less design simplifies agile development and dynamic data patterns.
Scalability
DynamoDB wins in extreme scalability. It supports millions of operations per second across partitions effortlessly.
Aurora scales well but still depends on instance class limits and readable replicas.
Query Language
Aurora uses full SQL- queries, joins, aggregations, stored procedures, indexes, etc.
DynamoDB supports PartiQL and key-based queries, but joins and complex relational logic aren’t native.
Performance
Aurora shines with transactional, high-performance relational workloads. DynamoDB, on the other hand, maintains steady millisecond latency at any scale due to its distributed, horizontally scalable architecture.
When To Choose AWS Aurora & DynamoDB
Choosing between Aurora and DynamoDB depends entirely on your data patterns, application logic, and performance requirements.
Use Aurora if:
Your data is highly structured and relational.
Applications with relationships, constraints, and predictable data structure work best with Aurora.
You need complex SQL queries, joins, or aggregations.
Analytical and transactional systems lean heavily on SQL.
You require strict ACID compliance.
Aurora guarantees consistent, reliable transactions; perfect for financial, e-commerce, or enterprise systems.
You need strict transactional integrity.
Aurora ensures every transaction is handled with full consistency and reliability, making it a strong fit for financial systems, e-commerce platforms, and enterprise applications where accuracy is non-negotiable.
You need strong read consistency across replicas.
Aurora’s storage layer ensures tight synchronization across AZs.
Use cases: OLTP systems, ERP, CRM, authentication services, SaaS platforms.
Use DynamoDB if:
You need massive scale with single-digit millisecond latency.
DynamoDB is built for extreme workloads without performance degradation.
Your schema is flexible or frequently evolving.
Ideal for semi-structured or document-style data.
Your access patterns are predictable and key-based.
DynamoDB shines in primary-key access models.
Your app must scale automatically across regions.
DynamoDB Global Tables support active-active architectures.
Use cases: IoT platforms, gaming leaderboards, mobile apps, serverless apps, real-time analytics pipelines.
Need Expert Help Choosing Your AWS Database?
Choosing the right AWS database can significantly impact performance, cost, scalability, and speed. That’s where Rapyder comes in. As a Premier Partner with AWS, we help businesses analyze their workloads, define the right data models, and select the best-fit database services across the AWS ecosystem.
Whether you’re looking to adopt Amazon Aurora for transactional workloads or DynamoDB for massive scale and low-latency applications, we guide you end-to-end; from architecture design to migration and optimization.
Conclusion
The Amazon Aurora vs DynamoDB debate isn’t about which database is better, it’s about which database is right for your workload. Aurora is perfect for relational, SQL-driven systems requiring strong consistency and complex queries. DynamoDB is ideal for unstructured data, massive scale, low latency, and flexible schemas.
Understanding your application’s requirements, access patterns, performance needs, consistency expectations, and growth plans, is the key to choosing the right AWS database. And if you need help navigating that decision, the experts at Rapyder are ready to assist.







